If the U.S. exchange rate falls,
A) foreign products are now more expensive toforeigners.
B) foreign products are now cheaper to U.S. citizens.
C) U.S. products are now more expensive to U.S. citizens.
D) U.S. products are now cheaper to foreign countries.
Ans: D) U.S. products are now cheaper to foreign countries.
You might also like to view...
The sum of the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and the marginal propensity to save (MPS) is
A) equal to one. B) greater than one. C) negative. D) less than one.
Pension plans, because of the __________-term nature of their liabilities, prefer to hold __________-term assets
A) long; long B) long; short C) short; long D) short; short
Assume that the government increases spending and finances the expenditures by borrowing in the domestic capital markets. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and current international transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index rises, and current international transactions become more negative (or less positive). b. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. c. The GDP Price Index rises, and current international transactions become more positive (or less negative). d. The GDP Price Index and current international transactions remain the same. e. The GDP Price Index falls, and current international transactions become more negative (or less positive).
Hotelling's model has been used to describe differentiation in the political "market." Suppose that 100 voters are evenly distributed between the extreme left and the extreme right on the political spectrum, and that all voters vote, and they always vote for the candidate closest to them on this spectrum. The numbers on this spectrum represent the number of voters lying to the left of the number. So, at the midpoint, fifty voters lie to the left and fifty to the right.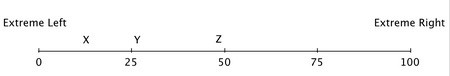 To an economic naturalist, this model helps explain why political candidates:
To an economic naturalist, this model helps explain why political candidates:
A. move toward more centrist positions during campaign season. B. work to bring federally funded projects to their home districts. C. take more extreme positions than are held by the general population. D. are loyal to their political parties.