Lukin Corporation reports the following first year production cost information.
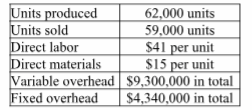
a. Compute production cost per unit under variable costing.
b. Compute production cost per unit under absorption costing.
c. Determine the cost of ending inventory using variable costing.
d. Determine the cost of ending inventory using absorption costing.
a. $41 DL + $15 DM + ($9,300,000/62,000) VOH = $206 per unit under variable costing
b. $206 + ($4,340,000/62,000) FOH = $276 per unit under absorption costing
c. (62,000 units - 59,000 units) × $206 per unit = $618,000 ending inventory under variable costing
d. (62,000 units - 59,000 units) × $276 per unit = $828,000 ending inventory under absorption costing
You might also like to view...
A credit crunch occurs when
A. banks do not lend as they ordinarily would, but rather have much higher requirements for borrowers to qualify for loans than normal. B. inflation rises, driving up interest rate near their legal ceiling, causing people to pull their funds out of banks. C. regulators pressure banks to increase loans to under-served groups in society. D. government officials force banks to lend in areas where they wish to establish branches.
Which of the following steps in the segmentation process involves determining the demographics, lifestyles, and usage behaviors that make one segment meaningfully different from another?
A) segment strategy "acid test" B) segment positioning C) segment attractiveness D) segment profitability E) segment identification
Companies that compete on an international basis have a competitive advantage over their purely domestic rivals
A. solely for the benefit of their shareholders. B. to give full access to the proprietary technological expertise or other competitively valuable capabilities. C. that guarantees the generation of big profits, big returns on investment, and big cash surpluses after dividends are paid. D. to benefit from coordinating activities across different countries' domains. E. to achieve a larger domestic interest by developing sufficient resource strengths and competitive capabilities for success.
A principal factor that the courts consider in determining limitations on the causal connection between the defendant's negligence and the plaintiff's injury is:
a. negligence per se. b. unforeseeable consequences. c. superseding causes. d. Both unforeseeable consequences and superseding causes are factors.