Some nonprice determinants of supply are:
A. prices of related goods, technology, and consumer preferences.
B. expectations of sellers and number of buyers in the market.
C. consumer preferences, the price of the good, and prices of related goods.
D. prices of related goods, technology, prices of inputs, expectations, and the number of sellers.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a reason why we should consider the federal national debt a problem?
A) If the debt was incurred to finance research and development, crowding out will occur. B) If the debt drives up interest rates, crowding out will occur. C) The federal government is in danger of defaulting on its debt. D) If the debt was incurred to finance improvements in infrastructure, crowding out will occur.
An increase in government spending by $100 would, if the MPC = 0.90, result in an increase in real GDP by:
a. $1,000. b. $9,000. c. $900. d. $190. e. inadequate information is given.
If an increase in income leads to an increase in the demand for sushi, then sushi is
A) a normal good. B) a neutral good. C) a complement. D) a necessity.
Refer to the table. Suppose that Libra decided to import more U.S. products. We would expect the quantity of libras:
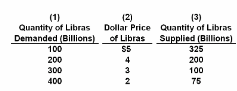
Answer the question on the basis of the following table, which indicates the dollar price of libras, the currency used in the hypothetical nation of Libra. Assume that a system of freely floating exchange rates is in place.
A. demanded at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.
B. demanded at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
C. supplied at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
D. supplied at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.