Two thin 80.0-cm rods are oriented at right angles to each other. Each rod has one end at the origin of the coordinates, and one of them extends along the +x-axis while the other extends along the +y-axis
The rod along the +x-axis carries a charge of -15.0 µC distributed uniformly along its length, and the other rod carries +15.0 µC uniformly over its length. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electrical force that these two rods exert on an electron located at the point (40.0 cm, 40.0 cm). (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, ?0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N • m2)
1.35 × 10-13 N at 135° with respect to the +x-axis
You might also like to view...
The figure shows the graph of 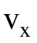 versus time for an object moving along the x-axis. Solve graphically for the distance traveled from t = 9.0 s to t = 13.0 s.
versus time for an object moving along the x-axis. Solve graphically for the distance traveled from t = 9.0 s to t = 13.0 s.
A. 60 m
B. 84 m
C. 76 m
D. 80 m
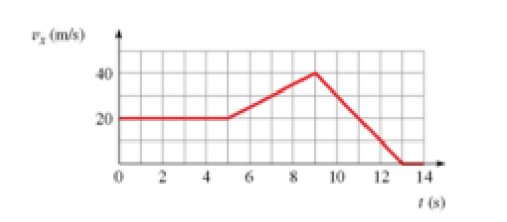
The heat conduction equation in cylindrical coordinates is
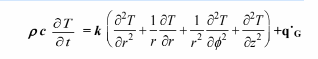
(a) Simplify this equation by eliminating terms equal to zero for the case of steady-state heat flow
without sources or sinks around a right-angle corner such as the one in the accompanying
sketch. It may be assumed that the corner extends to infinity in the direction perpendicular to
the page. (b) Solve the resulting equation for the temperature distribution by substituting the
boundary condition. (c) Determine the rate of heat flow from T1 to T2. Assume k = 1 W/(m K)
and unit depth .
GIVEN
• Steady state conditions
• Right-angle corner as shown below
• No sources or sinks
• Thermal conductivity (k) = 1 W/(m K)
FIND
(a) Simplified heat conduction equation (b) Solution for the temperature distribution (c) Rate of heat flow from T1 to T2 ASSUMPTIONS
• Corner extends to infinity perpendicular to the paper
• No heat transfer in the z direction
• Heat transfer through the insulation is negligible
SKETCH
If the maximum possible accuracy in measuring the energy of a particle increases, the maximum possible accuracy in measuring its lifetime will
A) increase. B) decrease. C) not be affected.
The principle of equivalence is primarily concerned with which of the following: