An advantage of using galvanized sheet metal over other materials when assembling a duct system is it
_____.
a. is very quiet
b. is resistant to corrosion
c. is the least expensive
d. exhibits the lowest heat loss
b
You might also like to view...
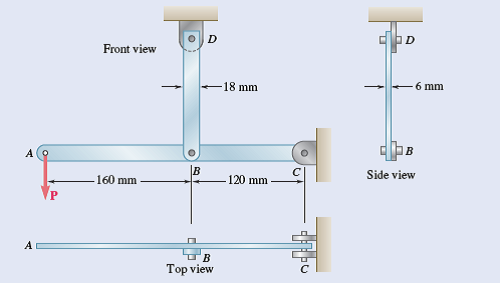
Problem 1.54 Solve Prob. 1.53, assuming that the structure has been redesigned to use 12-mm-diameter pins at B and D and no other change has been made. Problem 1.53 In the steel structure shown, a 6-mm-diameter pin is used at C and 10-mm-diameter pins are used at B and D. The ultimate shearing stress is 150 MPa at all connections, and the ultimate normal stress is 400 MPa in link BD. Knowing that a factor of safety of 3.0 is desired, determine the largest load P that can be applied at A. Note that link BD is not reinforced around the pin holes.
Use the finished drawing from Problem P12–4 to complete this problem. Create three cross sections through the new road and determine the cut and fill. Use the following information for this problem:
Cut three cross sections perpendicular through the road and cut and fill at the following locations: cross section A, 220? along the road centerline from point A; cross section B, 415? from cross section A, or at the widest area of fill; cross section C, 450? along the road centerline from the PI at point B. Locate completed cross sections on separate ANSI C size sheets, one section per sheet. The vertical scale of the cross sections is to be the same as the horizontal scale. The road surface has a slope of 0.02 ft./ft. from the road centerline. The shoulder surface has a slope of 0.06 ft./ft. from the edge of pavement (EOP). Exaggerate the road and shoulder surface slope angle on the drawing for clarity. The road has the following composition: 12?? thick base of gravel (show as dashed line); 6?? thick sand–asphalt hot mix (show as solid line); 1 1/4?? thick asphaltic–concrete surface (show as thick solid line). Draw cross sections with an appropriate scale that allows the drawing, especially the area of cut and fill, to be shown as large as possible on the sheet. Each cross section sheet may have a different scale. Label the centerline of the proposed road, bearings and distances, and location points on the road. Label the road width, shoulder width, road surface and shoulder surface slopes, and the centerline of the road in all cross sections. Label the road composition in all cross sections as local notes or called out on one sheet in general notes, with local note references on each drawing. Indicate cut and fill in cross sections with a note and show the angle of repose symbol and values on each side of the road, along the appropriate slope. Below all three cross section viewing arrow symbols on the base drawing, place a drawing reference in parentheses. For example, section A-A, if shown on sheet number P12–8–02, should have the label (P12–8–02) below one of the viewing arrows. Place a similar cross-reference label on the cross section drawing just below the section name. Use an appropriate graphic pattern to indicate areas of undisturbed Earth only. Place patches of this symbol at angular changes of undisturbed Earth and several places along slopes. Title all cross section drawings HWY. CROSS SECTION. Change the title of original map to HIGHWAY CUT AND FILL. Begin drawing numbers with P12–8–01 on the HIGHWAY CUT AND FILL drawing and continue in sequence with cross sections. Label the sheets as a set, such as 1 of 4, 2 of 4, and so on. Submit drawings plotted to scale on ANSI C size sheets, complete with border and title block.
Which of the following is not a vegetative control for lawns?
A) artificial propagation B) seeding C) sprigging D) plugging
The term ____ refers to how long a device is on over a given period of time.
A. encryption B. duty cycle C. power consumption