A small gas laser of the type used in classrooms may radiate light at a power level of 2.0 mW
If the wavelength of the laser light is 642 nm, how many photons does it emit per second? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s)
6.5 × 1015
You might also like to view...
Using your results from Problem 4.8, find the heat flow at the base of the fin for the following conditions:
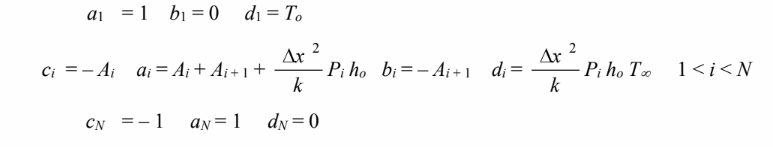
Use a grid spacing of 0.5 cm.
GIVEN
A fin with variable cross-sectional area and perimeter
FIND
(a) Heat flow rate for conditions given above
Energy Conservation With Conservative Forces: A bead is moving with a speed of 20 m/s at position A on the track shown in the figure. This track is friction-free, and there is no appreciable air resistance. What is the speed of the bead at point C?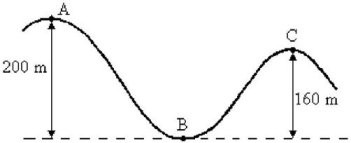
A. 0 m/s B. 34 m/s C. 69 m/s D. 20 m/s E. We cannot solve this problem without knowing the mass of the bead.
Why are Saturn's rings so thin?
A) They are attached to Saturn's very thin equator. B) The "gap" moons shepherd the particles and maintain its thin profile. C) Any particle in the ring with an orbital tilt would collide with other ring particles. D) Solar radiation pressure keeps particles pressed into the rings. E) They formed from a flat sheet of material that broke apart.
A 5-turn square loop (10 cm along a side, resistance = 4.0 ?) is placed in a magnetic field that makes an angle of 30° with the plane of the loop. The magnitude of this field varies with time according to B = 0.50t2, where t is measured in s and B in T. What is the induced current in the coil at t = 4.0 s?
A. 25 mA B. 5.0 mA C. 13 mA D. 43 mA E. 50 mA