If the quantity of money demanded is less than the quantity supplied at a given interest rate, what will happen to restore the market to equilibrium?
a. The public will try to buy bonds, the price of bonds will increase, and the interest rate will fall until the equilibrium is attained where the money demand and supply curves intersect.
b. The public will try to sell bonds, the price of bonds will decrease, and the interest rate will rise until equilibrium is attained where the money demand and supply curves intersect.
c. The public will try to sell bonds, the price of bonds will increase, and the interest rate will fall until equilibrium is attained where the money demand and supply curves intersect.
d. The public will try to buy bonds, the price of bonds will increase, and the interest rate will rise until equilibrium is attained where the money demand and supply curves intersect.
e. The public will try to buy bonds, the price of bonds will decrease, and the interest rate will fall until equilibrium is attained where the money demand and supply curves intersect.
A
You might also like to view...
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.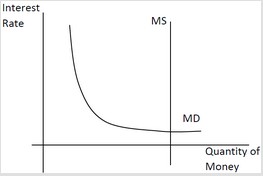 Based on this diagram, we can say ________.
Based on this diagram, we can say ________.
A. a contractionary policy is likely to be more effective than an expansionary policy B. the Fed is pursuing a contractionary monetary policy C. the Fed is pursuing an expansionary monetary policy D. an expansionary policy is likely to be more effect than a contractionary policy
The price that a person must pay in order acquire purchasing power now rather than in the future is called
a. the interest rate. b. the foreign exchange rate. c. the inflationary premium. d. the risk premium.
Most MNEs generate a majority of their revenues in their home regions.
a. true b. false
As you move up an indifference curve, the absolute value of the slope
A. remains constant. B. decreases. C. initially increases and then decreases. D. increases.