Use the following diagram to answer the next question.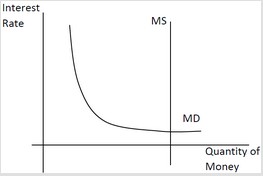 Based on this diagram, we can say ________.
Based on this diagram, we can say ________.
A. a contractionary policy is likely to be more effective than an expansionary policy
B. the Fed is pursuing a contractionary monetary policy
C. the Fed is pursuing an expansionary monetary policy
D. an expansionary policy is likely to be more effect than a contractionary policy
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
One practical implication of a kinked market supply curve is that:
A) producer surplus is not defined at the kink point. B) the MC = MR rule does not hold at the kink point. C) the market supply elasticity for a price increase may be different than the market supply elasticity for a price decrease at the kink point. D) All of the above are true.
Figure 13-4
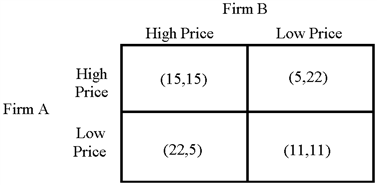
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is an argument against the idea that tariffs are necessary to protect against dumping?
a. It is difficult to assess whether a country is dumping its products or simply has lower production costs. b. Products dumped by foreign suppliers are usually outdated and pose no threat to domestic suppliers. c. It is considered more important to stockpile foreign goods to maintain supply during a war. d. Tariffs are not needed to counter dumping because environmental laws are in place to punish violators.
What determines the economic rent for land? Explain from a supply and demand perspective
What will be an ideal response?