The lifetime of a lightbulb in a certain application is normally distributed with mean µ = 1400 hours and standard deviation ? = 200 hours.
a. What is the probability that a lightbulb will last more than 1800 hours?
b. Find the 10th percentile of the lifetimes.
c. A particular lightbulb lasts 1645 hours. What percentile is its lifetime on?
d. What is the probability that the lifetime of a lightbulb is between 1350 and 1550 hours?
e. Eight lightbulbs are chosen at random. What is the probability that exactly two of them have lifetimes between 1350 and 1550 hours?
(a) z = (1800-1400)/200=2.00 . The area to the right of z= 2.00 is 0.0228.
(b) The z-score of the 10th percentile is ? ?1.28.
The 10th percentile is therefore ? 1400 ? 1.28(200) = 1144.
(c) z = (1645-1400)/200=1.23 . The area to the left of z= 1.23 is 0.8907.
Therefore a lifetime of 1645 is on the 89th percentile, approximately.
(d) For 1350, z = (1350-1400)/200=-0.25 . For 1550, z= (1550 ? 1400)/200 = 0.75.
The area between z= ?0.25 and z= 0.75 is 0.7734 ? 0.4013 = 0.3721.
(e) Let X be the number of bulbs with lifetimes between 1350 and 1550 hours. Using part (d), the probability that a bulb has a lifetime between 1350 and 1550 hours is 0.3721. Therefore X~Bin(8, 0.2721).
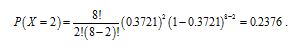
You might also like to view...
There are four estimates made for the anticipated cycle time to produce a subcomponent. The estimates, in seconds, are 10, 20, 30, and 70. If the first two estimates have equal weights, which total 70%, and the last two are weighted equally with the remaining 30%, what is the expected time?
What will be an ideal response?
A series RLC circuit has R = 10 ?, L = 2 mH, and C = 40 ?F. Determine the effective current and average power absorbed when the applied voltage is v(t) = 100 cos 1000t + 50 cos 2000t + 25 cos 3000t V
What will be an ideal response?
A 12 volt test light is a good tool for testing voltage levels
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
What is the accuracy of a D/A converter?
A) It is the comparison between the actual output of the converter and its expected output. B) It is the deviation between the ideal straight-line output and the actual output of the converter. C) It is the reciprocal of the number of discrete steps in the D/A output. D) It is the ability to resolve between forward and reverse steps when sequenced over its entire range of inputs.