Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.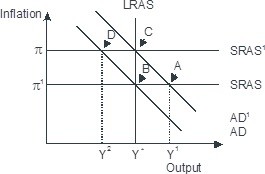
A. B; no output
B. D; an expansionary
C. B; recessionary
D. D; a recessionary
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The following table shows Alex's estimated annual benefits of holding different amounts of money.Average moneyholdings($)Total benefit($)700508005990066100071110074How much money will Alex hold if the nominal interest rate is 4 percent? (Assume she wants her money holdings to be in multiples of $100.)
A. $800 B. $700 C. $900 D. $1,000
Suppose the U.S. Congress is successful in enacting tariffs large enough to eliminate the current account deficit. What would happen to the level of domestic investment?
A) It would not change. B) It would fall to a level equal to national saving. C) It would rise and exceed national saving. D) It would rise to a level equal to net foreign investment.
Ethan enjoys buying books and going to the movies. He has income of $150 to spend on these two goods each month. The price of a book is $15 and the price of going to the movies is also $15. He currently consumes four books and six movies a month. If the price of a book increases to $20, then:
A. the substitution and income effects would both predict Ethan would consume less of both goods. B. the substitution effect would predict Ethan would consume more books and less movies, and the income effect would predict he would consume less of both. C. the substitution and income effects would both predict Ethan would consume more of both goods. D. the substitution effect would predict Ethan would consume less books and more movies and the income effect would predict he would consume less of both.
The current Debt to GDP level in the U.S.
A) is higher than they it has ever been B) is the highest in the world C) is about 100% D) grows at about $10 billion per year