An individual seller in perfect competition will not sell at a price lower than the market price because
A) the seller can sell any quantity she wants at the prevailing market price.
B) demand for the product will exceed supply.
C) the seller would start a price war.
D) demand is perfectly inelastic.
A
You might also like to view...
What important lesson did American economists learn in the 1980s and again in 2001–2003?
A. Large tax cuts can lead to a balance of trade surplus. B. Large government budget deficits can crowd out consumption. C. Large government budget deficits can bankrupt the nation. D. Large government budget deficits can crowd out net exports.
Refer to Common Property I. If access to the common property cannot be prohibited, then the resulting social gain equals
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.
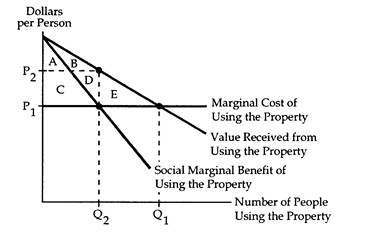
a. zero.
b. area E.
c. area A + B.
d. area C + D.
If the APC is 1.3, the APS is
A. -0.3. B. 0. C. 0.3. D. 0.7.
A monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve because
A) it is able to control price and quantity demanded. B) there are few substitutes for its product. C) of product differentiation. D) its market decisions are affected by the decisions of its rivals.