In the proton-proton cycle, the helium atom and neutrino have less mass than the original hydrogen. What happens to the "lost" mass?
A) It is recycled back into hydrogen.
B) It is ejected into space.
C) It is converted to energy.
D) It is transformed into electrons.
E) Conservation of mass dictates no mass can be lost.
C
You might also like to view...
Consider a conducting bar that is free to slide along conducting rails in an upward magnetic field as shown in the diagram below. If we connect the rails to the battery shown, which way will the bar be pushed?
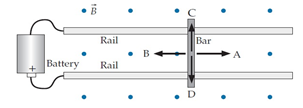
A.A
B.B
C.C
D.D
E. Down into the rails
F. Up off the rails
At what frequency should a 200-turn, flat coil of cross sectional area of 300 cm2 be rotated in a uniform 30-mT magnetic field to have a maximum value of the induced emf equal to 8.0 V?
a. 7.5 Hz b. 7.1 Hz c. 8.0 Hz d. 8.4 Hz e. 16 Hz
What eventually halts the gravitational collapse of an interstellar gas cloud that forms an object that is not massive enough to become a star?
A) Nothing; all collapsing gas clouds become black holes. B) the crowding of electrons in the core C) A critical fraction of the gas has been driven further into space. D) the central object becoming hot enough to sustain nuclear fusion in its core
It is common to illustrate the density of nuclear matter be discussing the mass of a teaspoon of nuclear material. What do nuclear densities imply for the mass of a teaspoon (5 cm3) of nuclear material? You may wish to use the relationship r=(1.2 fm)A1/3 together with the mass of a proton, 1.67 x 10-27 kg, to estimate.
A. 3.8 x 1011 kg B. 9.6 x 1011 kg C. 1.53 x 1012 kg D. 1.15 x 1012 kg