Consider a conducting bar that is free to slide along conducting rails in an upward magnetic field as shown in the diagram below. If we connect the rails to the battery shown, which way will the bar be pushed?
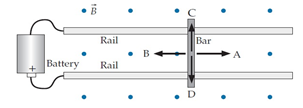
A.A
B.B
C.C
D.D
E. Down into the rails
F. Up off the rails
A.A
You might also like to view...
A copper-nickel alloy is used in a heat exchanger for a power plant that uses ocean water for cooling. One way to check the consistency of the alloy’s composition across batches of material is to determine the lattice parameter of the alloy. We know that copper and nickel are both FCC crystals and that copper and nickel form a limited-solid solution, and also that the lattice parameter of the alloy depends upon the composition. To determine the lattice parameter of the alloy, the angles of the diffraction peaks from a polycrystalline piece of the alloy are measured in an x-ray diffractometer with a cobalt x-ray tube. Cobalt is used because the cobalt K? radiation is of a lower energy than is the absorption edge in either copper or nickel, and no characteristic x-rays will be generated
in the copper and nickel. Also, the copper and nickel should be relatively transparent to the cobalt K? radiation. With the cobalt K? radiation, the lowest angle intense peak is measured at 25.74°. The lattice parameter of copper is 0.361 nm and for nickel it is 0.352 nm, and the wavelength of cobalt K? radiation is 0.1790 nm. (a) What are the Miller indices of this peak, and what is the lattice parameter of this copper-nickel mixture? (b) Assuming that the lattice parameter varies linearly with composition in this alloy, what is the percent of nickel and copper?
The sum of vectors A and B is

a. 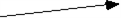
b. 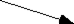
c. 
d. 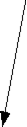
When the voltage across a steady resistance is doubled, the current
A) is half. B) remains the same. C) is doubled. D) is quadrupled.
The neon atom tends not to lose any electrons because
A) of its relatively strong effective nuclear charge. B) that would result in a negative ion. C) its electrons are paired together within the same orbitals. D) the ionization energy is so high.