Since Einstein, scientists think that the substance that is "waving" when a light wave is transmitted is
A) phlogisten.
B) air.
C) ether.
D) plasma.
E) They don't think any material substance is waving.
E
You might also like to view...
The greenhouse effect occurs on Earth because carbon dioxide is
a. transparent to visible light and opaque to infrared radiation. b. opaque to visible light and transparent to infrared radiation c. totally opaque to both visible light and infrared radiation d. totally opaque to both visible light and infrared radiation
The arrow in the photo on the left points to the location of the star that has exploded as a supernova in the photo on the right. Suppose you had looked with your naked eye at the supernova on the night it was photographed in the "during/after" photo. Assuming that it was bright enough to see (it was), what would it have looked like to your naked eye?
A) like a single star in the night sky B) like a huge white blob, about the angular size of the full Moon but not quite as bright C) like a reddish cloud spread out over a region of the sky about half the angular size of the full moon D) like a pulsating bright light, dimming and brightening about every 5 minutes
If Q = 20 ?C and L = 60 cm, what is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on any one of the charges shown?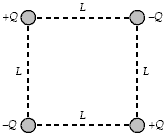
A. 25 N B. 19 N C. 15 N D. 9.1 N E. 14 N
It can be shown that the change in entropy in heating or cooling a sample is given by the relation src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/4efdbe7f0e8622ad72.png" class="w-image" />C?
A. +2.93 J/K
B. +2.50 J/K
C. 0 J/K
D. -2.93 J/K = mc ln
= mc ln 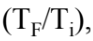 where m is the mass of the sample, c is the specific heat of the sample, and
where m is the mass of the sample, c is the specific heat of the sample, and 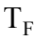 and
and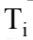 are the final and initial temperatures respectively. What is the change in entropy when 20.0 grams of aluminum with a specific heat of 0.9 J/gm K is heated from 10.0
are the final and initial temperatures respectively. What is the change in entropy when 20.0 grams of aluminum with a specific heat of 0.9 J/gm K is heated from 10.0 C 60.0
C 60.0