If a natural disaster were to cause a negative long-run supply shock to the economy, once the economy adjusts, the new equilibrium will be at a:
A. higher price level and lower level of output.
B. lower price level and lower level of output.
C. higher price level and higher level of output.
D. lower price level and higher level of output.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A difference between the classical and new classical models is that
a. classical economists assumed that labor suppliers knew the real wage, while the new classical economists assume they form a rational expectation of the real wage. b. classical economists assumed that the money wage was flexible while the new classical economists assume it was fixed. c. new classical models do not assume perfect competition. d. labor supply in the classical model is a function of the real wage while labor supply depends on the money wage in the new classical model. e. both a and c.
The opportunity cost of moving from point T to point Q would be
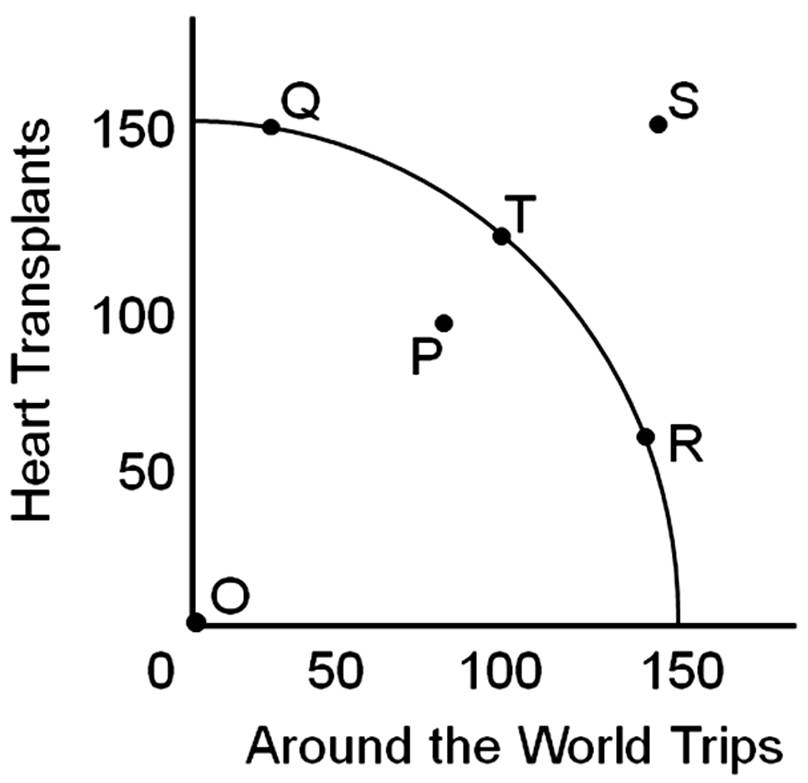
A. giving up trips around the world.
B. giving up heart transplants.
C. gaining trips around the world.
D. gaining heart transplants.
If computers and software are complements, then
A) a fall in the price of computers will increase the demand for software and, ceteris paribus, the price of software will rise. B) a rise in the price of computers will decrease the demand for software and, ceteris paribus, the price of software will rise. C) a fall in the price of computers will decrease the demand for software and, ceteris paribus, the price of software will fall. D) a rise in the price of software will increase the demand for computers and, ceteris paribus, the price of computers will rise. E) a fall in the price of software will decrease the demand for computers and, ceteris paribus, the price of computers will fall.
When growth goes down, unemployment tends to go:
A. down at the same time, and vice versa. B. up at the same time, but remains sticky on the way down and lags behind. C. down shortly after, and vice versa. D. up shortly after, and vice versa.