Making a decision "on the margin" involves comparing:
A. additional benefits against additional costs.
B. total benefits against total costs, which include benefits and costs from past decisions.
C. sunk costs against opportunity costs.
D. the most benefit you could expect to get without considering costs.
A. additional benefits against additional costs.
You might also like to view...
Exhibit 4-8 Demand and supply curves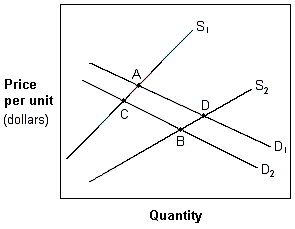
A. increase in the quantity supplied and a decrease in the demand. B. decrease in the quantity supplied and a decrease in demand. C. decrease in the quantity supplied and an increase in demand. D. decrease in the quantity demanded and a decrease in supply.
If a positive permanent supply shock were to occur, the resulting equilibrium would be a:
A. higher level of output at lower prices. B. lower level of output and prices. C. higher level of output and prices. D. lower level of output at higher prices.
When there's a shortage in the number of jobs available when teenagers look for summer jobs, the type of unemployment that arises is called
A. Frictional unemployment. B. Seasonal unemployment. C. Structural unemployment. D. Cyclical unemployment.
In a currency swap two parties agree to exchange flows of different bonds during a specified time period.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)