A thin, flat plate integrated circuit of 5 mm thickness is cooled on its upper surface by a dielectric liquid. The heat dissipation rate from the chip is 20,000 W/m2 and with the coolant flow at a free stream temperature of T?,l =250C, the convective heat transfer coefficient between the chip surface and the liquid is 1000 W/(m2 K). On the lower surface, the chip is attached to a circuit board, where the thermal contact resistance between the chip and the board is 10-4 m2.K/W. The thermal conductivity of board material is 1.0 W/m. K, and its other surface ( away from the chip) is exposed to ambient air at T?,a =200C where it is cooled by natural convection with the heat transfer coefficient of 30 W/(m2 K). (a) Determine the chip surface temperature under steady state condition for the
described conditions. (b) If the maximum chip temperature is not to exceed 750C, determine maximum allowable heat flux hat is generated by the chip. (c) A colleague suggests that in order to improve the cooling, you use a high conductivity bonding base at chip-board interface that would reduce the thermal contact resistance at the interface to 10-5 m2.K/W. Determine the consequent increase in the chip heat flux that can be sustained.
GIVEN

FIND
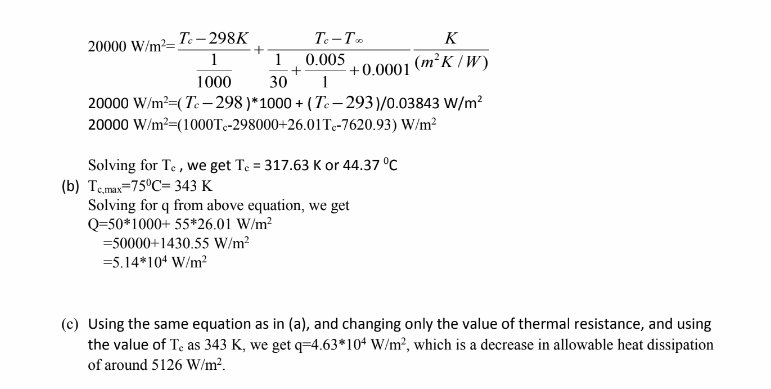
(a) Chip surface temperature under steady state condition
(b) Maximum allowable heat flux generated by the chip
(c) Consequent increase in chip heat flux if high conductivity bonding is used.
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state conditions prevail
The thermal conductivity of the wall (k) is constant
One dimensional conduction
Negligible radiation and thermal resistance between chip surface and the liquid.
SKETCH
The thermal circuit of problem is given by
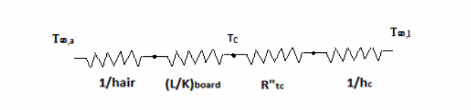
(a) A heat balance in the above problem gives
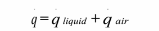
You might also like to view...
Blue light hitting a red sweatshirt is an example of
A) emission. B) reflection or scattering. C) transmission. D) absorption.
A light bulb is connected to a battery as shown in Figure A below. When a second bulb is connected as shown in Figure B, what happens to the brightness of the original bulb?
At the instant a 2.0-kg particle has a velocity of 4.0 m/s in the positive x direction, a 3.0-kg particle has a velocity of 5.0 m/s in the positive y direction. What is the speed of the center of mass of the two-particle system?
a. 3.8 m/s b. 3.4 m/s c. 5.0 m/s d. 4.4 m/s e. 4.6 m/s
An object is at rest on the equator. Estimate its speed relative to the center of the Earth in m/s
1.less than 0.001 2.between 0.001 and 0.01 3.between 0.01 and 0.1 4.between 0.1 and 1 5.between 1 and 10 6.between 10 and 100 7.between 100 and 1,000 8.between 1,000 and 10,000 9.more than 10,000 10.Impossible to determine