The annual income that can be consumed without diminishing the total capital assets of a nation is
(a) purchasing power parity income.
(b) sustainable national income.
(c) environmental capital stock.
(d) per capita income.
B
You might also like to view...
How does an economic model attempt to explain puzzling behavior? What features would be desirable in an economic model?
What will be an ideal response?
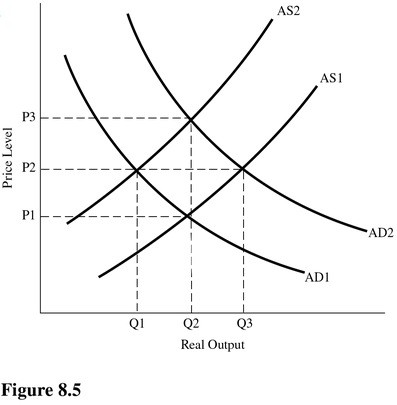 Using Figure 8.5, if the equilibrium price level is P1, then aggregate demand is
Using Figure 8.5, if the equilibrium price level is P1, then aggregate demand is
A. AD2, and the equilibrium output level is Q2. B. AD2, and the equilibrium output level is Q1. C. AD1, and the equilibrium output level is Q2. D. AD1, and the equilibrium output level is Q3.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 33.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.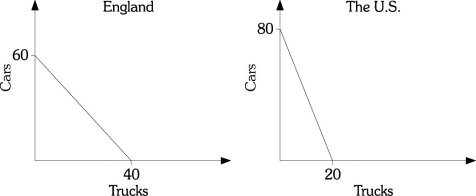 Figure 33.2Refer to Figure 33.2. the U.S. has
Figure 33.2Refer to Figure 33.2. the U.S. has
A. no comparative advantage in producing either cars or trucks. B. a comparative advantage in producing trucks. C. an absolute advantage in producing trucks. D. a comparative advantage in producing cars.
Refer to the graphs below. In Graph B, assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at point x1 but then there is an increase in the price level from P1 to P2. In the long run, this change will lead to:
In the graphs below, QP refers to the economy's potential output level.
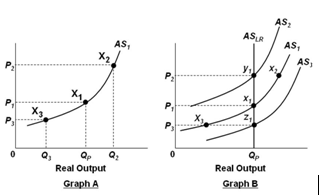
A. Lower nominal wages and a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2
B. Higher nominal wages and a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2
C. Lower nominal wages and a movement from equilibrium point x1 to equilibrium point x2
D. Higher nominal wages and a movement from equilibrium point x1 to equilibrium point x2