In the classical model, high unemployment due to a change in aggregate demand
A) can persist for an indefinite period of time.
B) will return to its normal level quickly as wages adjust.
C) will persist if due to a supply shock but not if due to a demand shock.
D) never exists because unemployment can never deviate from its normal level.
B
You might also like to view...
If a negative externality exists, then there is a __________ when society produces the market output instead of the socially optimal output. This exists because the __________ to sellers and third parties are __________ the __________ derived by buyers.
A. net social benefit; costs; greater than; benefits B. net social cost; benefits; less than; costs C. net social cost; costs; greater than; benefits D. net social cost; costs; less than; benefits E. none of the above
When the British pound rises in value relative to other currencies, then
A) goods imported into Britain rise in price. B) British exports rise in price. C) neither British exports nor imports rise in price. D) both British exports and imports rise in price.
Which of the following examples is shown in this graph?
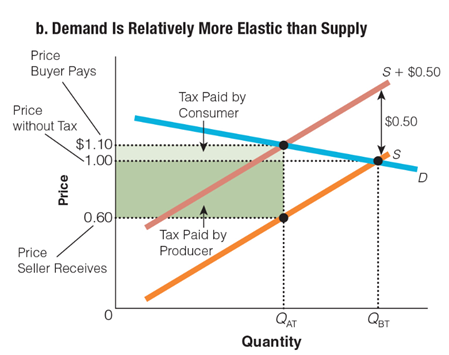
a. The buyer pays $0.50 of a $0.50 tax.
b. The buyer pays $0.40 of a $0.50 tax.
c. The seller pays $0.50 of a $0.50 tax.
d. The seller pays $0.40 of a $0.50 tax.
Refer to Scenario 9.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow. SCENARIO 9.5: Investors put up $520,000 to construct a building and purchase all equipment for a new restaurant. The investors expect to earn a minimum return of 10 percent on their investment. The restaurant is open 52 weeks per year and serves 900 meals per week. The fixed costs are spread over the 52 weeks (i.e. prorated weekly). Included in the fixed costs is the 10% return to the investors and $1,000 per week in other fixed costs. Variable costs include $1,000 in weekly wages and $600 per week for materials, electricity, etc. The restaurant charges $3 on average per meal. Refer to Scenario 9.5. In the short run, if the restaurant shuts down, its losses will equal its ________ costs of ________.
A. variable; $1,600 B. fixed; $2,000 C. total; $3,600 D. fixed; $1,000