Determine the temperature at the four nodes shown in the sketch. Assume steady conditions and two-dimensional heat conduction. The four faces of the square shape are each at different temperatures as shown.
GIVEN
Square shape with four different face temperatures
FIND
Temperature at four interior nodes
SKETCH
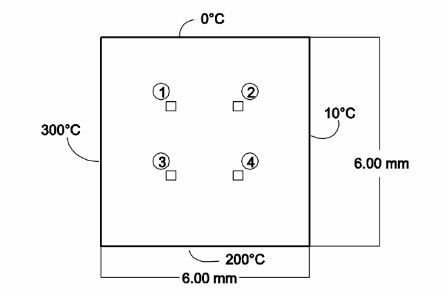
If the shape is divided into square control volumes then according to, the temperature at
each node is the average of its four neighbors. The equation for each node is therefore
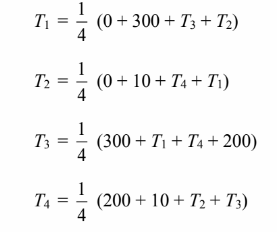
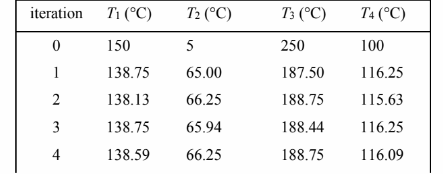
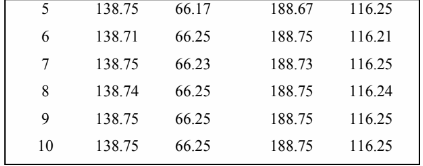
The equations can be solved by the iterative method. A table showing the calculation for the first 10
iterations is given below. The zero iteration is the initial guess of the temperature at the four nodes.
You might also like to view...
In a contest, two tractors pull two identical blocks of stone the same distance over identical surfaces. However, block A is moving twice as fast as block B when it crosses the finish line. Which statement is correct?
A. Block A has twice as much kinetic energy as block B. B. Block B has lost twice as much kinetic energy to friction as block A. C. Block B has lost twice as much kinetic energy as block A. D. Both blocks have had equal losses of energy to friction. E. No energy is lost to friction because the ground has no displacement.
A photon of initial wavelength 0.651 nm, after being scattered from a free electron at rest, moves off at an angle of 120° with respect to its incident direction
(mel = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s) (a) What is the wavelength of the scattered photon? (b) What is the energy of the scattered photon?
To analyze single-slit diffraction, what new assumption not made in the Young double-slit experiment must be made?
1.Each portion of the slit acts as a source of light waves. 2.The light's wavelength is at the red end of the spectrum. 3.Interference effects can be ignored. 4.The distance between the slit and the screen is much greater than the wavelength of the light.
In a completely inelastic collision between two objects where the mass of one is double that of the other, which of the following statements is always true?
a. The larger mass will always lose kinetic energy. b. The smaller mass will always gain kinetic energy. c. The momentum of the smaller mass will have a larger magnitude change than that of the larger mass. d. Not even one of the above statements is true.