The firm's short-run supply curve begins at an output of
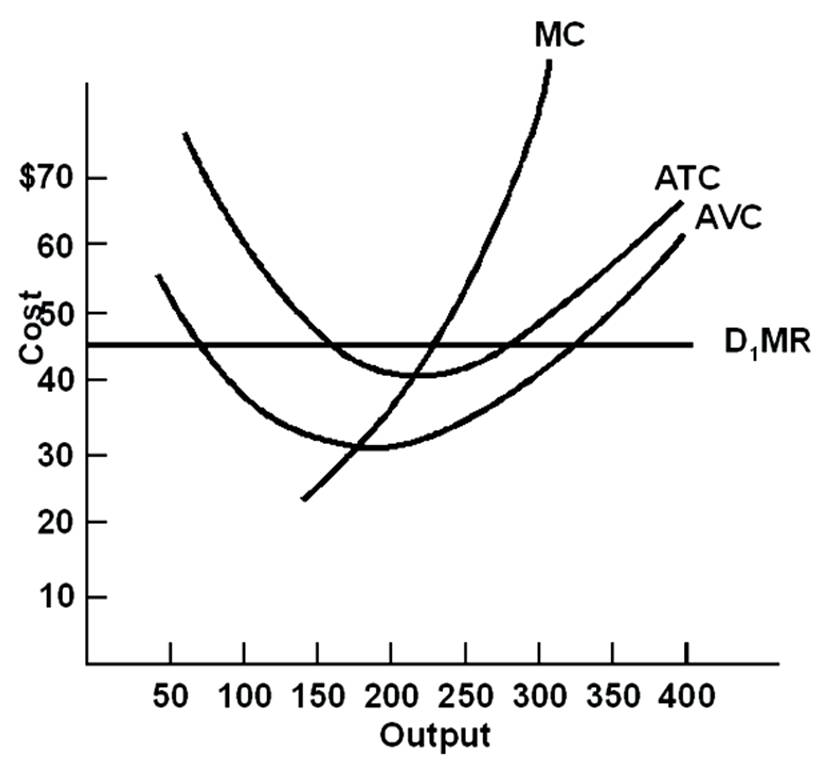
A. 100.
B. 175.
C. 250.
D. 300.
B. 175.
You might also like to view...
The following table provides data for an economy in a certain year. Consumption expenditures1,000Imports600Government purchases of goods and services700Construction of new homes and apartments500Sales of existing homes and apartments600Exports500Government payments to retirees200Household purchases of durable goods300Begining-of-year inventory500End-of-year inventory600Business fixed investment300Given the data in the table, compute the value of GDP.
A. 2,700 B. 2,400 C. 2,500 D. 2,600
The long-run supply curve of an industry equals the industry’s
A. long-run marginal cost curve. B. the horizontal sum of all firms’ supply curves at any point in time. C. long-run average cost curve. D. long-run total variable cost curve.
If tax revenues equal 20 percent of total output and government expenditures equal 25 percent of total output, then there is a:
A. trade surplus. B. trade deficit. C. government budget deficit. D. government budget surplus.
The most efficient method of allocating scarce resources is through:
a. well-placed price controls on high-cost goods and services. b. utilization controls to ensure that demand does not exceed supply. c. competitive markets that allow supply and demand to interact freely to establish equilibrium prices. d. strictly followed budgets that keep spending under control. e. favorable tax treatment on those items that policy makers want to control.