The U.S. inflation of the 1960s was spread overseas via the ________ exchange rates of the time and led to the ________ of the Bretton Woods system
A) fixed, collapse
B) fixed, establishment
C) flexible, collapse
D) flexible, establishment
A
You might also like to view...
The difference between absolute and comparative advantage is that:
a. absolute advantage refers to input cost, while comparative advantage refers to opportunity cost. b. absolute advantage refers to opportunity cost, while comparative advantage refers to input cost. c. absolute advantage is applicable only to individuals, and comparative advantage is applicable only to countries. d. absolute advantage is applicable only to countries, and comparative advantage is applicable only to individuals. e. absolute advantage is applicable to international trade, while comparative advantage applies to exchange of goods in the domestic market.
Refer to the graph shown.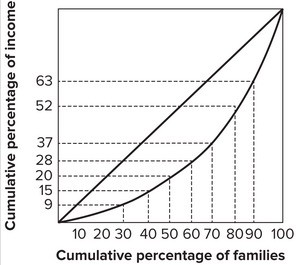 The poorest 30 percent of the families earn:
The poorest 30 percent of the families earn:
A. 9 percent of the income. B. 15 percent of the income. C. 2 percent of the income. D. 5 percent of the income.
If the market price is above the equilibrium price:
a. A surplus will occur and producers will produce less and lower prices b. Producers will make extremely high profits c. A surplus will result and consumers will bid prices up d. A shortage will occur and producers will produce more and lower prices
If, in the market for money, the amount of money supplied exceeds the amount of money households and businesses want to hold, the interest rate will:
A. fall, causing households and businesses to hold less money. B. rise, causing households and businesses to hold less money. C. rise, causing households and businesses to hold more money. D. fall, causing households and businesses to hold more money.