Monetary policy has an:
A. unambiguous effect on exchange rates because the income, price, and interest rate effects offset one another.
B. ambiguous effect on exchange rates because the income, price, and interest rate effects offset one another.
C. unambiguous effect on exchange rates because the income, price, and interest rate effects reinforce one another.
D. ambiguous effect on exchange rates because the income, price, and interest rate effects reinforce one another.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph of the demand for pasta to answer the question below.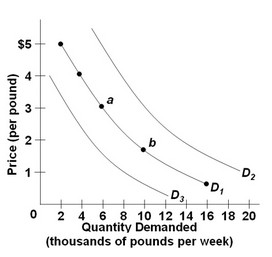 Refer to the three demand curves for pasta and assume that pasta is an inferior good. Which of the following would shift the demand for pasta from D1 to D3?
Refer to the three demand curves for pasta and assume that pasta is an inferior good. Which of the following would shift the demand for pasta from D1 to D3?
A. an increase in the price of pasta B. a decrease in consumer incomes C. an increase in consumer incomes D. a decrease in the price of pasta
Which of the following best describes an assumption economists make about human behavior?
A) They assume that people take into account the question of fairness in all decisions they make. B) They assume that individuals act rationally all the time in all circumstances. C) They assume that rational behavior is useful in explaining choices people make even though people may not behave rationally all the time. D) They assume that individuals act randomly.
Economists have long pondered the reasons why people hold money. Some reasons seem to be more important than others. Perhaps not among the most important but still a reason why people hold money is for emergency purposes (the idea of having money available for that "rainy day"). Economist refer to that demand for money as
a. precautionary b. emergency c. speculative d. transactions e. temporary
Profit can be defined as the
a. difference between the sales revenue of a business firm and the opportunity cost of the resources required to produce the goods supplied by the firm. b. difference between a company's income and direct monetary costs of production. c. difference between the price of a product and the consumer's valuation of the good. d. amount of total revenue earned by the firm minus its payments to stockholders.