If the world price of coffee is higher than Colombia's domestic price of coffee without trade, then Colombia
a. should import coffee.
b. has a comparative advantage in coffee and should export coffee.
c. should produce just enough coffee to satisfy domestic demand.
d. should produce no coffee domestically.
b
You might also like to view...
Refer to the above figure. If the relevant aggregate demand curve is AD1, then the economy is experiencing
A) full employment. B) an inflationary ga
Suppose ordinarily half your class would get an A and half would get a B, with A students having a 25% chance of getting an A and B students having a 25% of getting an A. It costs $100 to persuade the instructor to raise a B grade to an A. A student is willing to pay $40 to insure she will get her usual grade and $70 to insure she will get a higher grade than usual. a. Who would buy insurance and at what price in a competitive equilibrium?
b. Suppose it costs $5 to truthfully signal your type and $10 to falsely signal what type of student you are, and if an insurance company receives no signal, it will interpret this as a signal that you are a B student. What would be the competitive outcome now? c. Suppose a new teacher comes in -- and this teacher is willing to change a grade for just $60. How does your answer to (a) change? d. How would your answer to (b) change? e. Can you change something in the problem that would result in only A-students buying insurance? What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the accompanying figure, which shows the annual domestic supply and annual domestic demand for jeans in a small country.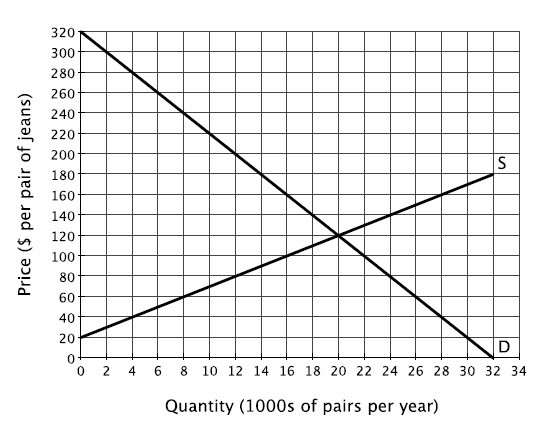 Suppose this country initially does not trade with the rest of the world. If the world price of a pair of jeans is $40, and this country opens itself to trade, then the annual domestic production of jeans will:
Suppose this country initially does not trade with the rest of the world. If the world price of a pair of jeans is $40, and this country opens itself to trade, then the annual domestic production of jeans will:
A. increase from 20,000 to 28,000. B. increase from 4,000 to 28,000. C. fall from 20,000 to 4,000. D. fall from 28,000 to 4,000.
GDP is the market value of:
A. all intermediate goods and services produced in an economy in a given year. B. all expenditures on consumption, investment, and net exports in an economy in a given year. C. all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given year. D. all expenditures on natural resources, labor, and capital goods in an economy in a given year.