A giant star radiates energy at the rate of 3.0 × 1030 W, and its surface temperature has been measured to be 3000 K. Assuming that it is a perfect emitter, what is the radius of this star? (? = 5.67 × 10-8 W/m2 ? K4)
A) 7.8 × 1010 m
B) 8.7 × 1010 m
C) 1.4 × 1010 m
D) 1.9 × 1011 m
E) 2.3 × 1011 m
E
You might also like to view...
If the intensity of radiation from the sun is 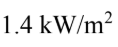 at a distance of
at a distance of 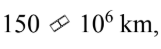 at what distance is the intensity
at what distance is the intensity 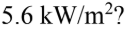
A. 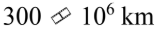
B. 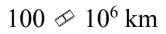
C. 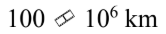
D. 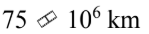
E. less than  km
km
In the most general form of the first law of diffusion, the gradient of the Gibbs free energy with respect to the position of B-type atoms is equal to the chemical _____________on the B-type atoms.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Constant Acceleration Kinematics: A bicyclist starts a timed race at 6.0 mi/h. In order to win, he must average 21 mi/h. Assuming constant acceleration from the start, how fast must he be traveling at the end of the race?
A. 36 mi/h B. 30 mi/h C. 24 mi/h D. 42 mi/h
A proton is located at the point (x = 1.0 nm, y = 0.0 nm) and an electron is located at the point Find the magnitude of the electrostatic force that each one exerts on the other. (k = 1/4??0 = 9.0 × 109 N ? m2/C2, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C)
A) 1.4 × 10-11 N B) 5.3 × 10-18 N C) 5.3 × 108 N D) 5.9 × 10-15 N