When the BEA calculates real GDP using the average of prices in the current year and the year preceding it, and this average changes from year to year, this is called calculating GDP using
A) chained-weighted prices.
B) fixed-weight prices.
C) current-year prices.
D) fixed base-year prices.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the accompanying figure. At P = 8 and Q = 4, D1 is ________ elastic than D2, which is shown graphically as D1 being ________ D2.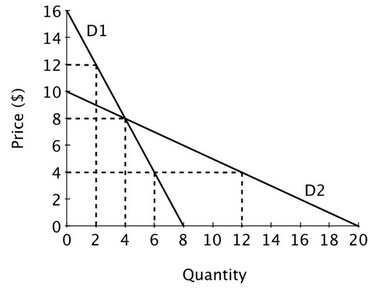
A. less; flatter than B. more; steeper than C. less; steeper than D. more; flatter than
Susie knows that too many sugary treats, while delicious when eaten, have long-term adverse effects on weight and health. Based on this information, a behavioral economist would expect Susie to:
A. carefully weigh the short-term benefits against the long-term costs and make a rational decision about how many treats to eat. B. eat more sugary treats than is optimal, as she likely gives more weight to present events and outcomes than to ones in the future. C. give away most of her sugary treats in an effort to resist temptation. D. compute the caloric intake and calculate how many hours of exercise would be needed to burn off the calories from each treat.
Assume that microbrewery beer is a normal good. Prices of microbrewery beer have risen steadily in recent years. Over this same period, prices for fermenting vats used in beer making have also risen and consumer incomes have fallen. Which of the
following best explains the rising prices of microbrewery beer? A) The supply curve for microbrewery beer has shifted to the left while the demand curve for microbrewery beer has shifted to the right. B) The demand curve for microbrewery beer has shifted to the left more than the supply curve has shifted to the left. C) The demand curve and the supply curve for microbrewery beer have both shifted to the right. D) The supply curve for microbrewery beer has shifted to the left more than the demand curve has shifted to the left.
________ is/are the market value of final goods and services produced within a country during a given period of time.
A. Consumption B. Value added C. GDP D. Transfer payments