When charge Q1 is placed at point P1, the resulting potential at point P is V1 . When Q2 is placed at point P2 after Q1 is in position at P1, the resulting potential at P becomes V2 . What is the potential at point P if charge Q1 is then removed?
a. V1 – V2
c. V1 + V2
b. (V1 + V2)/2
d. V2 – V1
D
You might also like to view...
A transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation z(y, t) = 1.50 cm sin(1,250 rad/s t + 10.0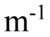 What is the velocity of the wave?
What is the velocity of the wave?
A. 125 m/s in the + z direction B. 250 m/s in the - z direction C. 125 m/s in the + y direction D. 125 m/s in the - y direction E. 250 m/s in the - y direction
The "seeing ability" or resolution of radiation is determined by its wavelength. If an atom is approximately 10?10 m in diameter, how fast must an electron travel to have a wavelength smaller than the size of an atom?
Assume that the average mass of each of the approximately 1 billion people in China is 55 kg. Assume that they all gather in one place and climb to the top of 2-m-high ladders. The center of mass of the Earth (mE = 5.90 1024 kg) is then displaced
a. 0 m. b. 1.84 × 10^?23 m. c. 1.84 × 10^?14 m. d. 1.80 × 10^?13 m. e. 2 m.
A disturbance in particle motion parallel to the wave velocity is called a
a. transverse wave. b. acoustic wave. c. standing wave. d. longitudinal wave.