Pigouvian taxation:
A. involves the use of taxes or fees to remedy negative externalities.
B. involves the use of subsidies to remedy negative externalities.
C. is a legal principle requiring a party who takes an action that harms others to compensate the affected parties for some or all of their losses.
D. requires that victims of an externality pay a tax to the producers of the externality.
A. involves the use of taxes or fees to remedy negative externalities.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant) average total cost. If she does not sell a cake the day she makes it, she sells it as day-old cake for $10. What is her expected marginal cost of holding the 22nd cake in inventory?
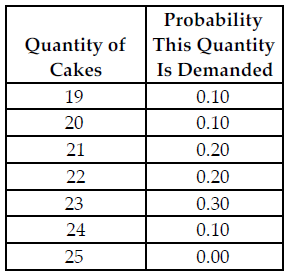
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
A) $0.40
B) $1.20
C) $0.80
D) $2.00
Critics of the supply-side tax cuts proposed by the Reagan administration argued that lower taxes would:
a. increase the budget deficit. b. decrease money supply in the economy. c. reduce the aggregate price level. d. reduce the disposable income of households. e. reduce the volume of international trade.
Pricing an option involves an application of all of the following except:
a. the Black-Scholes Model. b. the law of one price. c. the assumption that there are no unexploited profit opportunities. d. the assumed probability that the stock price will go up.
An unexpected decrease in the demand for accountants will lead to
a. an increase in the earnings of accountants. b. an increase in the incentive of students to prepare for a career in accounting. c. a reduction in the future supply of accountants. d. an increase in the employment opportunities of accountants.