Estimation by WLS
A) although harder than OLS, will always produce a smaller variance.
B) does not mean that you should use homoskedasticity-only standard errors on the transformed equation.
C) requires quite a bit of knowledge about the conditional variance function.
D) makes it very hard to interpret the coefficients, since the data is now weighted and not any longer in its original form.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Long-run cost functions are estimated using
A) time-series regression analysis. B) cross-sectional regression analysis. C) cost accounting data. D) None of the above
The long-run aggregate supply curve of an economy corresponds to
A) a point inside the production possibilities curve. B) a point outside the production possibilities curve. C) a point on the production possibilities curve. D) none of the above: there is no relationship between the long-run aggregate supply curve and the production possibilities curve.
Refer to the graph. A decrease in fixed costs is shown by:
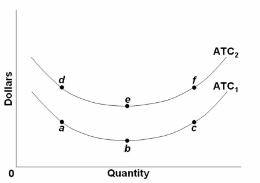
A. a move along short-run average total cost curve ATC 2 from point e to point f.
B. a move along short-run average total cost curve ATC 1 from point a to point b.
C. the shift of the short-run average total cost curve from ATC 1 to ATC 2 .
D. the shift of the short-run average total cost curve from ATC 2 to ATC 1
An increase in expected future output while holding today's output constant would
A. increase today's desired consumption and decrease desired national saving. B. decrease today's desired consumption and increase desired national saving. C. decrease today's desired consumption and decrease desired national saving. D. increase today's desired consumption and increase desired national saving.