Briefly describe why taxes create deadweight loss
When the government imposes a tax on a product, buyers and sellers allocate resources according to the tax incentive rather than the true costs and benefits of the good.
You might also like to view...
As the best measure of the size of economic fluctuations associated with a business cycle, economists typically use
A) real GDP. B) the deviation of real GDP from potential GDP. C) potential GDP. D) the deviation of real GDP from nominal GDP.
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a tax increase that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ and eventually to a long-run equilibrium at point ________, if left to self-correcting tendencies.
A. D; C B. D; B C. A; B D. B; C
A nation can produce two products: tanks and autos. The table below is the nation's production possibilities:
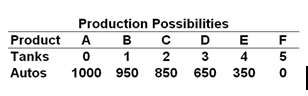
Given the production possibilities schedule above, a combination of 3 tanks and 350 autos:
A. Illustrates the tradeoff between tanks and autos
B. Is attainable but entails some unemployment or inefficient use of society's resources
C. Cannot be produced by society, given its current resources and production technology
D. Is not attainable because this combination is not listed in the schedule
If the quantity of goods and services produced in the economy decreases
A) it may be possible for real GDP to increase. B) real GDP would certainly increase. C) it may be possible for nominal GDP to increase. D) nominal GDP would certainly increase.