The ability of one person or nation to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another is called a(n)
A) market advantage. B) absolute advantage.
C) comparative advantage. D) specialization advantage.
C
You might also like to view...
Auctions are valuable for selling items such as
a. Pens b. Artwork c. Standard automobiles d. All of the above
Suppose the equilibrium price in the market is $10 and the price elasticity of demand for the linear demand function at the market equilibrium is ?1.25. Then we know that:
A. marginal revenue is $2. B. demand is unit elastic. C. marginal revenue is $50. D. demand is inelastic.
In reference to the long-run firm competitive equilibrium diagram, which of the following statements is INCORRECT?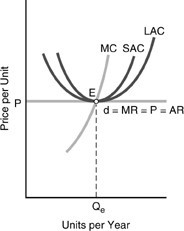
A. In the long run, the firm has no incentive to alter its scale of operations. B. In the long run, the firm operates where price, marginal revenue, marginal cost, short-run minimum average cost, and long-run minimum average cost all are equal. C. Because profits must be zero in the long run, the firm's short-run average costs (SAC) must equal P at Qe, which occurs at minimum SAC. D. In the long run, this firm must be part of a constant-cost industry, because its marginal revenue curve is perfectly elastic.
The most significant difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition is that
A. in a perfectly competitive market there is a small number of sellers, while in a monopolistically competitive market there is a large number of sellers. B. in a perfectly competitive market products are homogeneous, while in a monopolistically competitive market products are differentiated. C. in a perfectly competitive market there is a large number of sellers, while in a monopolistically competitive market there is a small number of sellers. D. in a perfectly competitive market products are differentiated, while in a monopolistically competitive market products are homogeneous.