A reduction in the real exchange rate indicates that
A) foreign goods are now relatively cheaper.
B) foreign goods are now relatively more expensive.
C) domestic goods are now relatively more expensive.
D) both A and C
B
You might also like to view...
During normal times, discretionary fiscal policy
A) is probably not very effective in influencing real GDP due to time lags. B) is more effective in influencing real GDP than automatic stabilizers. C) works well because there are no lag problems in influencing real GDP. D) is more effective in influencing real GDP than at times of a recession.
In the long run, economic profits are:
a. possible both for a monopolist and for a perfectly competitive firm. b. possible for a monopolist but not for a perfectly competitive firm. c. possible for a perfectly competitive firms but not for a monopolist. d. impossible for both a monopolist and for a perfectly competitive firm.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 29.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.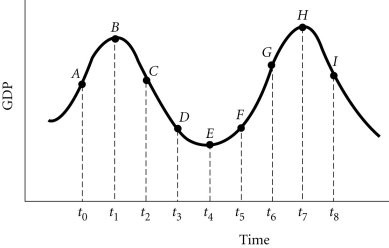 Figure 29.1Refer to Figure 29.1. If the condition of the economy at Point H is realized by policy makers when the economy is at Point I, policy is likely to be inappropriate due to
Figure 29.1Refer to Figure 29.1. If the condition of the economy at Point H is realized by policy makers when the economy is at Point I, policy is likely to be inappropriate due to
A. the implementation lag. B. the response lag. C. crowding out. D. the recognition lag.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.1 below for the economy of Macroland to answer the question(s) that follow.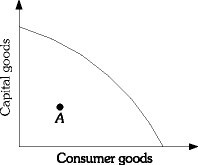 Figure 2.1Refer to Figure 2.1. If Macroland's economy is at Point A, it could produce more consumer goods
Figure 2.1Refer to Figure 2.1. If Macroland's economy is at Point A, it could produce more consumer goods
A. only with technological improvements. B. only with additional resources. C. without sacrificing any capital goods. D. only by sacrificing some capital goods.