Assume that the supply of coffee in a competitive market decreases. What will most likely happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of coffee?
a. Price will increase; quantity will increase
b. Price will decrease; quantity will increase
c. Price will increase; quantity will decrease
d. Price will decrease; quantity will decrease
Answer: c. Price will increase; quantity will decrease
You might also like to view...
Using trade restrictions to protect special interests such as the U.S. auto industry
A) results in lower prices for U.S. auto consumers. B) raises the prices that U.S. consumers must pay for autos. C) is a very cost-efficient way of dealing with trade problems. D) is the best long-term solution for threatened U.S. jobs.
According to the graph shown, if this were a perfectly competitive market, the outcome in the short run would be:
This graph shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly.
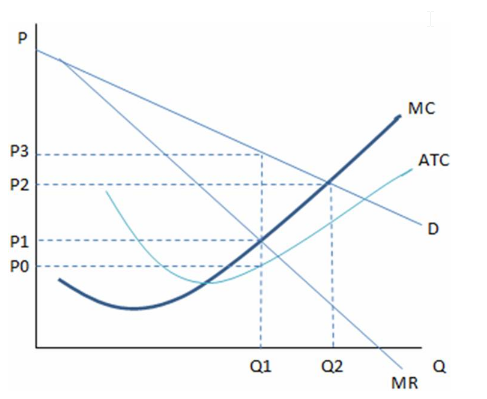
A. Q1, P1.
B. Q1, P3.
C. Q2, P2.
D. The graph is of a monopoly, and therefore there is no way to determine a perfectly competitive outcome.
The demand curve for capital:
a. shows the positive relation between capital usage and the quantity of capital demanded. b. shows the positive relation between aggregate output and the quantity of capital demanded. c. shows the negative relation between rate of inflation and the quantity of capital demanded. d. shows the positive relation between technological change and the quantity of capital demanded. e. shows the negative relation between price of capital and the quantity of capital demanded.
Why might firms experience diseconomies of scale?
What will be an ideal response?