Two flat rectangular mirrors are set edge to edge and placed perpendicular to a flat nonreflecting surface. The edges of the two mirrors meet at a 30° angle. A light ray that approaches mirror 1 is parallel to mirror 2 . The angle of reflection of that ray from mirror 1 is
a. 0°
b. 30°.
c. 60°.
d. 90°.
e. 120°.
c
You might also like to view...
A mass m = 4.0 kg is connected, as shown, by a light cord to a mass M = 6.0 kg, which slides on a smooth horizontal surface. The pulley rotates about a frictionless axle and has a radius R = 0.12 m and a rotatinal inertia I = 0.090 kg?m2. The cord does not slip on the pulley. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of m?
?
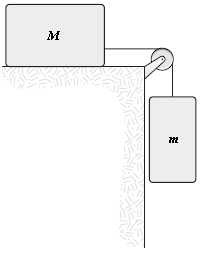
A. ?2.4 m/s2 B. ?2.8 m/s2 C. ?3.2 m/s2 D. ?4.2 m/s2 E. ?1.7 m/s2
The position of a particle as a function of time is given by x(t) = (3.5 m/s)t - (5.0 m/s2)t2. What is the average velocity of the particle between t = 0.30 s and t = 0.40 s?
What will be an ideal response?
For glucose dissolving in water at 298 K, the diffusivity is 6.9 x 10^-10m^2/s. What do you expect the diffusivity of water in glucose to be?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is not a scalar quantity?
a. Kinetic energy b. Potential energy c. Power d. Work e. None of these; that is, they are all scalar quantities.