Refer to the table above. Suppose investment is $12 billion and the economy revises its saving plans so as to save $4 billion less at all levels of income. The new equilibrium GDP will be:
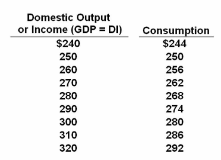
All figures below are in billions of dollars.
A. $260 billion
B. $270 billion
C. $280 billion
D. $290 billion
D. $290 billion
You might also like to view...
Refer to Monopoly Problem. This monopoly will receive producer surplus of
Consider a monopoly with constant marginal costs of $20. Consumers in the market for this monopoly’s product have demand of Q = 100 - 2P. a. $0 b. $225 c. $450 d. $900
The primary reason that short-lived shocks can have long-run effects is
A) the nonneutrality of money. B) misperceptions by the public over the actual price level and the expected price level. C) the presence of rational expectations among the public. D) the presence of propagation mechanisms.
The effectiveness of direct controls on pollution depends on: (i) the budgets and enthusiasm of the regulatory bodies; (ii) sufficiently strong statutory penalties
a. i and ii b. i but not ii c. ii but not i d. neither i nor ii
Refer to the accompanying figure. Suppose the solid line shows the current demand for coffee. In response to news that next year's coffee harvest will be extremely good due to favorable weather conditions, you should expect: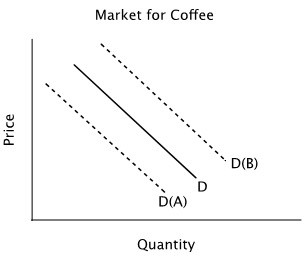
A. the quantity of coffee demanded to decrease, but no shift in the demand curve. B. the demand curve to shift to D(B) in anticipation of lower future prices. C. the demand curve to shift to D(A) in anticipation of lower future prices. D. neither a change in quantity demanded nor a shift in demand because it will be a long time before next year's coffee crop is harvested.