Rational expectations theory is also known as the Friedman fooling theory
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
False
You might also like to view...
Suppose Chris is offered the following gamble: with probability 0.1 he will win $90, with probability 0.4 he will win $50, and with probability 0.5 he will lose $60. The expected value of this gamble is ________.
A. $1 B. $2 C. -$1 D. $0
Many economists believe that if fiscal policy turns contractionary to reduce the deficit,
A. monetary policy can turn expansionary to counteract the effects on aggregate demand. B. monetary policy must be contractionary to reinforce the good effects of contractionary fiscal policy. C. foreign investment in the United States must be encouraged. D. taxes on the earnings from stock market gains should be increased.
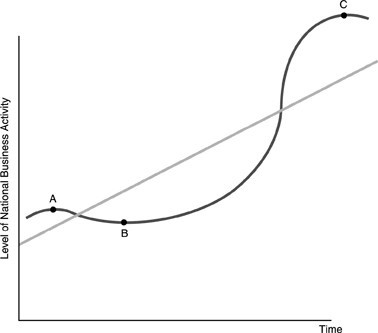 Refer to the above figure. The points between B and C are known as
Refer to the above figure. The points between B and C are known as
A. a peak. B. a trough. C. an expansion. D. a contraction.
A monopolist sells a homogeneous good in several distinct submarkets, and the elasticities of demand differ in these submarkets. If the monopolist selects the rate of output to sell in each submarket by equating marginal revenue and marginal cost, then
A) all customers in all markets end up paying the same price. B) it is not price discriminating, but merely price differentiating. C) customers in markets with more elastic demand will pay higher prices than customers in markets with less elastic demand. D) customers in markets with more elastic demand will pay lower prices than customers in markets with less elastic demand.