Refer to Figure 23-1. If the economy is at point J, what will happen?
A) Inventories have fallen below their desired level, and firms increase production.
B) Inventories have risen above their desired level, and firms increase production.
C) Inventories have risen above their desired level, and firms decrease production.
D) Inventories have fallen below their desired level, and firms decrease production.
A
You might also like to view...
The monetary stimulus post-September 11, 2001, achieved some desired effects within the year
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Which of the following is/are part of Fayol's 14 principles of management?
Will and Grace have adjoining unfenced back yards and each has just adopted a new puppy. Will values a fence between their yards at $250 and Grace values a fence between their yards at $200. The cost of building the fence is $300, which will be split equally if they both agree to build the fence. Therefore, their payoff matrix is as follows. If Will decides to build the fence, then Grace will earn a higher payoff by ________, and if Will decides to not build the fence, then Grace will earn a higher payoff by ________.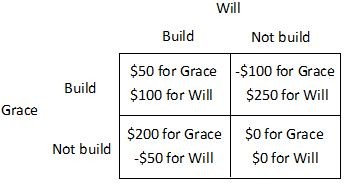
A. not helping to build the fence; also not building the fence B. helping to build the fence; also not building the fence C. not helping to build the fence; building the fence D. helping to build the fence; building the fence
Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the:
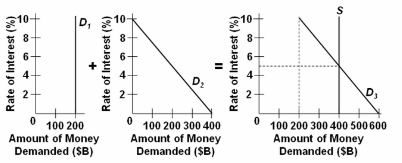
A. S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise.
B. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
C. D 3 would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
D. D 3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise.