A(n) __________________ is one-3,600th of a degree
a. precession
b. second of arc
c. minute of arc
d. nadir
e. angular diameter
B
You might also like to view...
Assume all else is unchanged, and the Earth's rotational axis is perpendicular to the ecliptic. As a result, seasonal variations on the Earth would
a. be practically non-existent. b. remain the same as they are at now. c. have the same severity but each season would last twice as long. d. be much more severe.
Air at an average temperature of 150°C flows through a short square duct 10 × 10 × 2.25 cm at a rate of 15 kg/h. The duct wall temperature is 430°C. Determine the average heat transfer coefficient, using the duct equation with appropriate L/D correction. Compare your results with flow-over-flat-plate relations.
GIVEN
• Air flowing through a short square duct
• Average air temperature (Ta) = 150°C
• Duct dimensions = 10 × 10 × 2.25 cm = 0.1 × 0.1× 0.0225 m
• Duct wall surface temperature (Ts) = 430°C
• Mass flow rate (m ) = 15 kg/h
FIND
The average heat transfer coefficient ( h c) using (a) The duct equation with appropriate L/D correction (b) The flow-over-flat-plate relation
ASSUMPTIONS
• Constant and uniform duct wall temperature
SKETCH
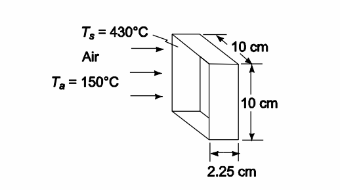
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the average temperature of 150°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0339 W/(m K)
Absolute viscosity (?b) = 23.683 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 At the surface temperature of 430°C,
the absolute viscosity (?s) = 33.66 × 10–6
A 16-kg mass is placed on a 25° incline and friction keeps it from sliding. The coefficient of static friction in this case is 0.574 and the coefficient of sliding friction is 0.519 . The mass is given a shove causing it to slide down the incline. Taking down the incline as positive, what is the acceleration of the mass while it is sliding?
a. 0.47 m/s2 b. –0.47 m/s2 c. –0.96 m/s2 d. 0.96 m/s2 e. 14.50 m/s2
A steel bracket ABC (EI 5 4.2 3 106 N # m2) with span length L 5 4.5 m and height H 5 2 m is subjected to load P 5 15 kN at C. The maximum rotation of joint B is approximately:
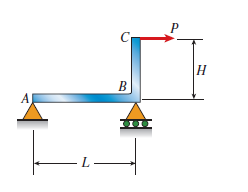
(A) 0.18
(B) 0.38
(C) 0.68
(D) 0.98