What effect does an increase in real GDP have on the demand for money?
What will be an ideal response?
An increase in real GDP increases the demand for money and shifts the demand for money curve rightward.
You might also like to view...
In the neoclassical growth model, convergence is conditional upon two countries having
a. the same savings rates. b. the same depreciation rates. c. the same technology growth rates. d. the same population growth rates. e. all of the above.
Which of the following statements is true?
a. The speculative demand for money at possible interest rates gives the demand for money curve its upward slope. b. There is an inverse relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate. c. According to the quantity theory of money, any change in the money supply will have no effect on the price level. d. All of these are true.
What happens to desired investment spending if the interest rate rises? Is this response relevant to the supply of loanable funds curve or the demand for loanable funds curve?
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.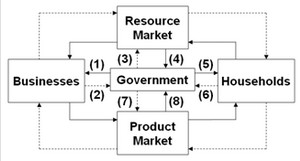 In the diagram, solid arrows reflect real flows and broken arrows are monetary flows. Flow (7) might represent
In the diagram, solid arrows reflect real flows and broken arrows are monetary flows. Flow (7) might represent
A. wage payments to public school teachers. B. subsidies to corporations to stimulate exports. C. a transfer payment to disabled persons. D. the U.S. Bureau of Engraving and Printing's expenditures for paper.