Normally, when a governmental price control affects the price, it can be expected to result in a
A. reduction in the number of units purchased only when the price is forced down.
B. reduction in the number of units purchased when the price is forced down and an increase number of units purchased when the price is forced up.
C. decrease in the number of units purchased when the price is forced up or down.
D. increase in the number of units purchased when the price is forced up or down.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Does the Invisible Hand Theorem remain true in the Prisoners' Dilemma game? Why or why not? What implication does this result have for cartels?
What will be an ideal response?
Assume that the government one day decides to tax greens fees at all state golf courses. To the government's dismay, not only was the amount of tax collected small, but there was a 90 percent decline in golfing
What type of tax analysis did the government apparently rely upon when it imposed this tax? A) static tax analysis B) dynamic tax analysis C) transaction cost analysis D) ad hoc tax analysis
Suppose a competitive market is comprised of firms that face identical cost curves. The firms experience an increase in demand that results in positive profits for the firms. Which of the following events are then most likely to occur? (i) New firms will enter the market. (ii) In the short run, price will rise; in the long run, price will rise further. (iii) In the long run, all firms will be
producing at their efficient scale. a. (i) and (ii) only b. (i) and (iii) only c. (ii) and (iii) only d. (i), (ii) and (iii)
Refer to the graph shown. If this graph represents a competitive market, the equilibrium price and quantity will be: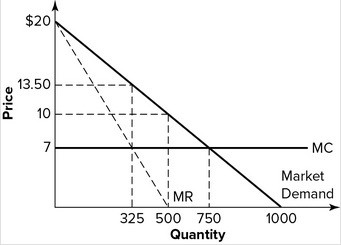
A. $13.50 and 325, respectively. B. $10 and 500, respectively. C. $7 and 750, respectively. D. $7 and 325, respectively.