In a perfectly competitive industry, firms are likely to:
A.) Exit when there are economic profits because they know the profits will not last.
B.) Reduce the level of production when there are economic profits.
C.) Enter when there are economic profits.
D.) Enter when price is equal to the minimum average total cost.
C.) Enter when there are economic profits.
You might also like to view...
Correlation of the regression error across observations
A) results in incorrect OLS standard errors. B) makes the OLS estimator inconsistent, but not unbiased. C) results in correct OLS standard errors if heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors are used. D) is not a problem in cross-sections since the data can always be "reshuffled."
If a toy store overestimates the demand for a toy in 2004 and, as a result, has an unexpectedly large number of toys in stock at the end of the year, the value of the inventory of these toys will be considered as: a. investment in 2004
b. investment in 2005. c. consumption in 2004. d. consumption in 2005. e. a part of GDP when the toys are sold.
Refer to Figure f. A benefit function is plotted in Figure f. The letter B represents the:
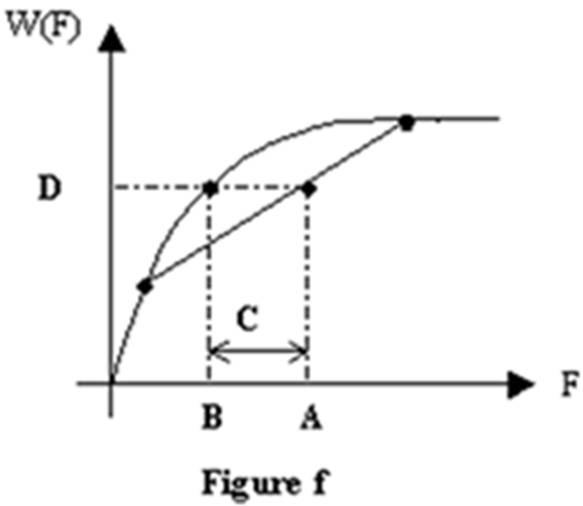
A. risk premium of the consumption bundle.
B. expected utility of the consumption bundle.
C. certainty equivalent of the consumption bundle.
D. expected consumption.
Aside from a statistical discrepancy, any deficit in the current account is matched by
A. a surplus in the merchandise trade balance. B. the excess of exports over imports. C. a deficit in the capital account. D. a surplus in the capital account.