If the nominal exchange rate e is foreign currency per dollar, the domestic price is P, and the foreign price is P*, then the real exchange rate is defined as
a. e(P/P).
b. e(P/P).
c. e + P/P.
d. e - P/P.
D
You might also like to view...
A $2 tax per gallon of paint placed on the buyers of paint will shift the demand curve
a. downward by exactly $2. b. downward by less than $2. c. upward by exactly $2. d. upward by less than $2.
Both open market purchases and quantitative easing are directed at increasing reserves in the banking system and increasing the money supply
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1 the result in the long run would be: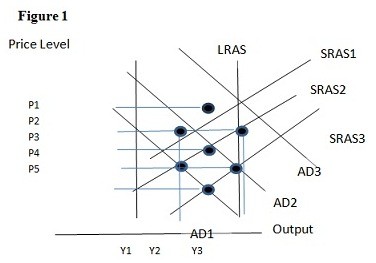
A. P4 and Y1. B. P4 and Y2. C. P5 and Y1. D. P5 and Y2.
Refer to the diagram. If the price level rises above P 1 because of an increase in aggregate demand, the:
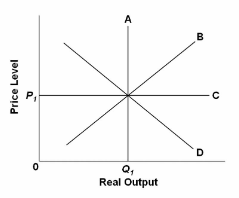
A. economy will move up along curve B and output will temporarily increase.
B. long-run aggregate supply curve C will shift upward.
C. short-run aggregate supply curve B will automatically shift to the right.
D. economy's output first will decline, then increase, and finally return to Q 1.