Refer to the diagram. If the price level rises above P 1 because of an increase in aggregate demand, the:
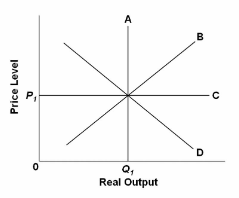
A. economy will move up along curve B and output will temporarily increase.
B. long-run aggregate supply curve C will shift upward.
C. short-run aggregate supply curve B will automatically shift to the right.
D. economy's output first will decline, then increase, and finally return to Q 1.
A. economy will move up along curve B and output will temporarily increase.
You might also like to view...
Which anti-discrimination law prohibits discrimination by employers on the basis of race, color, religion, gender, or national origin?
A) the Civil Rights Act of 1964 B) the Equal Employment Opportunity Act of 1972 C) the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 D) the Rehabilitation Act of 1973
The effects of a decrease in export demand
A) is a powerful argument in favor of fixed rates. B) is a powerful argument in favor of flexible rates. C) shows the difficulties in determining which exchange rate is better. D) is a powerful argument in favor of fixed rates only in the short run. E) is a powerful argument in favor of fixed rates only in the long run.
Under both perfect competition and monopoly, a firm:
A. is a price taker. B. is a price maker. C. will shut down in the short-run if price falls short of average total cost. D. sets marginal cost equal to marginal revenue.
If full employment GDP is $1 trillion greater than the equilibrium GDP and the multiplier is 5, how much is the deflationary gap?
What will be an ideal response?