A sample of helium (He) occupies 44.8 L at STP. What is the mass of the sample?
A)
2 g
B)
4 g
C)
6 g
D)
8 g
E)
10 g
D
You might also like to view...
Vega is an A0 main sequence star. Based on this information, which statement is true?
a. Vega has a surface temperature that is less than the Sun b. Vega has mass that is greater than the Sun c. Vega is less luminous than the Sun d. Vega has mass that is less than the Sun e. Vega is located near the lower right hand corner on the HR diagram
Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: As shown in the figure, a 1.45-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 21-N horizontal external force. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity v1 = 1.2 m/s as it separates from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity v2 = 2.1 m/s at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface is 0.29. The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. How much work is done by friction between points B and C?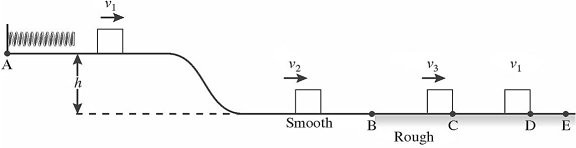
style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="148" width="576" /> A. -1.8 J B. -3.6 J C. -14 J D. -6.4 J E. -7.0 J
"Warp one" (the speed of light) is what Mach number at 20.°C?
What will be an ideal response?
How does gravitational lensing tell us about the mass of a galaxy cluster?
A) The lensing broadens spectral lines, and we can use the broadening to "weigh" the cluster. B) Using Einstein's general theory of relativity, we can calculate the cluster's mass from the precise way in which it distorts the light of galaxies behind it. C) The lensing allows us to determine the orbital speeds of galaxies in the cluster, so that we can determine the mass of the cluster from the orbital velocity law. D) Newton's universal law of gravitation predicts how mass can distort light, so we can apply Newton's law to determine the mass of the cluster.