Growth accounting, popularized by Robert Solow, attempts to attribute a change in aggregate output
A) to its most important single cause.
B) separately between changes in government policy and changes in total factor productivity.
C) separately between changes in total factor productivity and changes in the supplies of factors of production.
D) separately between changes in the supplies of factors of production and changes in government policy.
C
You might also like to view...
At all quantities, the demand curve for a monopolist generally
A. is steeper than the marginal revenue curve. B. lies below the marginal revenue curve. C. is the same as the marginal revenue curve. D. lies above the marginal revenue curve.
What happens to aggregate demand as the price level increases?
a. It increases. b. It decreases. c. It remains constant. d. It moves away from equilibrium.
A decrease in the price of foreign oil will affect the U.S. economy by
A. increasing aggregate demand. B. decreasing aggregate demand. C. increasing aggregate supply. D. decreasing aggregate supply.
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q total fixed cost is:
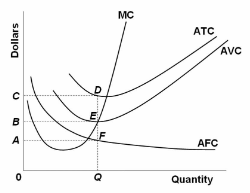
A. 0BEQ.
B. BCDE.
C. 0BEQ - 0AFQ.
D. 0CDQ.