What are the three strategies for defending against foreign organisms, cells, or molecules?
What will be an ideal response?
(1 ) Prevent foreign cells or molecules from entering the body. (2 ) Attack any foreign cell or molecule that enters the body. (3 ) Destroy the specific foreign cell or molecule that enters the body, and remember it.
You might also like to view...
What chemical initiates the formation of acid mine drainage when pyrite is not disposed of properly?
A) O2 B) Fe2+ C) HS- D) SO42-
Characteristic colonial morphology should include all of the following except:
a. glistening. b. fermenter. c. pinpoint. d. entire.
Dephosphorylation of the adenosine triphosphate molecule (shown in this diagram) generally results in only the removal of the Gamma phosphate and Beta phosphate groups, leaving the Alpha phosphate group bonded to the adenosine molecule. How can you explain this behavior?
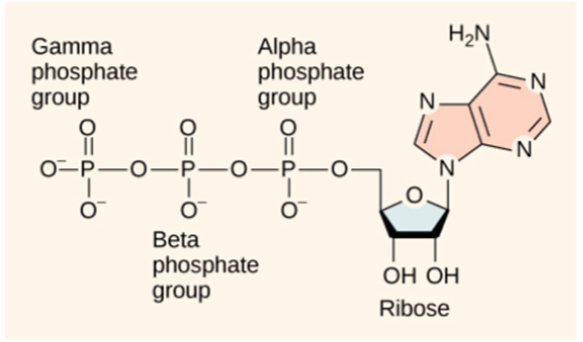
a. The enzymes that catalyze dephosphorylation reactions become saturated after bonding with two phosphate groups and cannot bond to a third.
b. After two phosphate groups are removed from ATP, the resulting solution is too acidic to sustain additional dephosphorylation reactions.
c. Without the repulsive forces generated between phosphate groups, the adenosine monophosphate molecule is much more stable.
d. Dephosphorylation can proceed with the Alpha phosphate group, but cells only require the energy released from Gamma and Beta phosphate groups.
As an adult, which of the following typical
chordate embryonic traits do adult tunicates retain?
a. hollow, dorsal nerve cord b. notochord c. gill slits d. tail extending beyond anus e. more than one of these