Which of the following does not help to explain why the US imports capital-intensive goods?
a) preference differences between nations
b) the imposition of tariffs
c) differences in technology across countries
d) the relatively recent development of the US capital-goods industry
e) imperfect competition
d) the relatively recent development of the US capital-goods industry
You might also like to view...
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 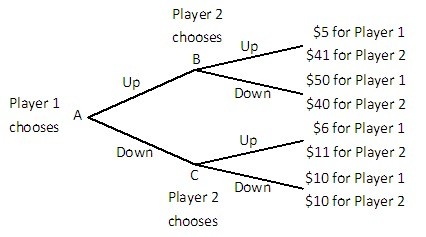 If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
A. Player 2 would commit to choosing Down. B. Player 2 would commit to choosing Up. C. Player 2 would not commit to choosing either strategy. D. Player 2 would commit to mimicking Player 1's strategy.
The demand for money increases and the demand curve for money shifts rightward as a result of
A) an increase in real GDP. B) a decrease in the price level. C) a decrease in the nominal interest rate. D) an increase in the use of credit cards. E) a decrease in the real interest rate.
If coal and oil are substitute inputs in the production of electricity, an increase in the price of oil
a. will increase the demand for coal. b. will reduce the demand for coal. c. will increase the supply of coal. d. will reduce the supply of coal. e. will not affect the demand for coal.
If either the production or consumption of a good generates an external cost, then the:
A. social demand curve will lie to the right of the private demand curve. B. social demand for the good will equal zero. C. social marginal cost curve will lie to the left of the private marginal cost curve. D. social marginal cost curve will lie to the right of the private marginal cost curve.