All natural monopolies are characterized by
a. decreasing marginal cost at the point where their marginal cost curve crosses their demand curve.
b. the fact that they earn economic losses.
c. decreasing average costs at the point where their average cost curve crosses their demand curve.
d. the fact that losses can only be avoided if they are regulated.
c. decreasing average costs at the point where their average cost curve crosses their demand curve.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. If the discount rate is 5 percent and the cost of the investment is $43,000, which of the following is true regarding a profit-maximizing manager?
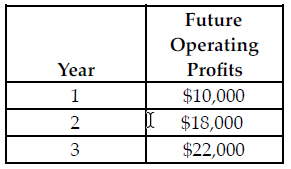
The above table shows the future operating profits from an investment. The future operating profits are earned at the end of each of the respective years.
A) The manager should not make the investment because the net present value is positive.
B) The manager should make the investment because the net present value is positive.
C) The manager should not make the investment because the net present value is negative.
D) The manager should make the investment because the net present value is negative
Advocates of antipoverty programs claim that
a. the government has good information about what people are willing to pay to eliminate poverty. b. fighting poverty is a public good. c. private sector will incur higher costs than the public sector for these programs. d. All of the above are correct.
Subsidies are most likely to:
A. increase total economic surplus. B. reduce consumer surplus. C. reduce total economic surplus. D. leave total economic surplus unchanged, but transfer surplus from producers to consumers.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 28.7 below to answer the question(s) that follow.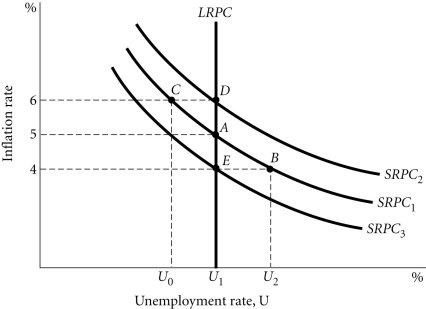 Figure 28.7Refer to Figure 28.7. Which combinations of events could move the economy from Point A to Point B, and then from Point B to Point E?
Figure 28.7Refer to Figure 28.7. Which combinations of events could move the economy from Point A to Point B, and then from Point B to Point E?
A. an expansionary fiscal policy followed by a leftward shift in the AS curve B. a contractionary monetary policy followed by a rightward shift in the AS curve C. an expansionary fiscal policy followed by a rightward shift in the AS curve D. a contractionary monetary policy followed by a leftward shift in the AS curve