The following graph represents the concentration of cyclins over the course of the cell cycle. Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the phase of the cell cycle where the blue arrow is pointing?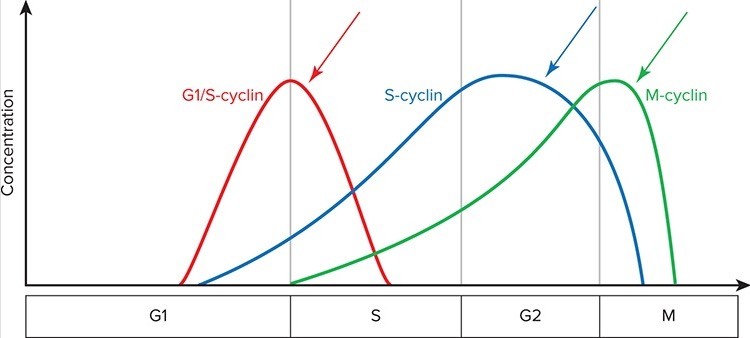 McGraw-Hill Education
McGraw-Hill Education
A. At this point in the cycle the cell is determining if environmental conditions are favorable for growth and proliferation.
B. At this point in the cell cycle, DNA has already been replicated and divided into two daughter nuclei.
C. At this point in the cell cycle, chromosomes have properly aligned on the metaphase plate and are beginning to separate.
D. At this point in the cycle the cell is continuing to grow and make abundant tubulin proteins.
E. At this point in the cell cycle, the cell has determined that the DNA is intact, that environmental conditions are favorable, and it is preparing for DNA replication.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Consider three different enzymes (identified as 1-3, below), each of which has a unique complement of three amino acids that are crucial for the binding of the substrate at the active site
Select from choices A-D the characteristic you would predict a substrate would possess that would bind to an active site where these amino acids are present. (Consult Figure 4.2 in Chapter 4 to help you make your predictions.) Enzyme 1: leucine, tryptophan, and alanine A. relatively hydrophobic B. hydrophilic, with a negative charge C. hydrophilic, with a positive charge D. hydrophilic, but without a charge
The drug(s) used to treat genital herpes is/are
A. penicillin. B. erythromycin. C. acyclovir. D. famciclovir. E. acyclovir AND famciclovir
What percentage of Florida's species are exotics?
a. 25 b. 78 c. 65 d. 10 e. 45
Carbon dioxide has what effect on systemic arterioles?
A) vasoconstriction B) vasodilation C) neither vasodilation or vasoconstriction, but may cause vasospasm D) vasoconstriction and vasospasm E) vasospasm