For many years, China tightly managed its currency through intervention and capital controls, effectively pegging the yuan to the U.S. dollar (a rate of about 8 yuan per dollar). Which of the exchange rate regimes discussed in the textbook did China have at that time?
A. Purchasing-power-parity exchange rate
B. Fixed exchange rate
C. Flexible exchange rate
D. Partially-flexible exchange rate
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
You are on a vacation in a foreign country. Because it is your first visit to the country, you do not know much about the tourist spots. So you decide to ask the manager of the hotel regarding the popular tourist places
He tells you that there is a waterfall and a beautiful park close to the hotel that you can visit. You are wondering which place to go to when you overhear some of the tourists planning a trek to one of the falls. You decide to join them. This is an example of a(n) ________. A) moral hazard B) adverse selection C) pecuniary externality D) information cascade
Which one of the following is not a component of GDP, as measured using the expenditure approach?
a. Personal consumption. b. Exports. c. Durable goods. d. Government spending. e. Interest.
Four firms are major manufacturers in different industries. Which firm is likely in an oligopolistic market?
a. Firm A finds that increasing its output raises its average total cost. b. Firm B competes against many rivals in its industry. c. Firm C earns zero long-run economic profit. d. Firm D is uncertain about its marginal revenue curve.
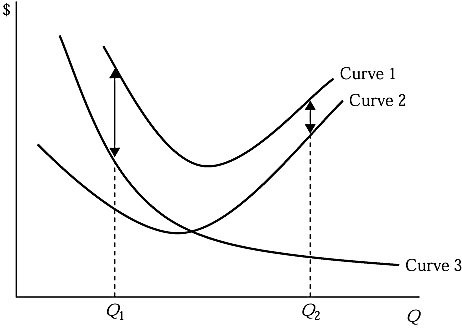
 Refer to Figure 5.2, which shows a family of average cost curves. The average total cost curve is represented by:
Refer to Figure 5.2, which shows a family of average cost curves. The average total cost curve is represented by:
A. Curve 1. B. Curve 2. C. Curve 3. D. the vertical sum of curve 1 and curve 2.